Mitigation Blocks
Mitigation Blocks are an important concept in
Smart Money Concepts trading, helping traders identify key price zones
Mitigation Blocks Complete Easy to Understand
Mitigation Blocks are an important concept in Smart Money Concepts (SMC) trading, helping traders identify key price zones where institutional traders revisit to mitigate or reconcile unfilled orders. Mastering mitigation blocks can improve your trade entries, risk management, and understanding of market behavior.
1. What Is a Mitigation Block?
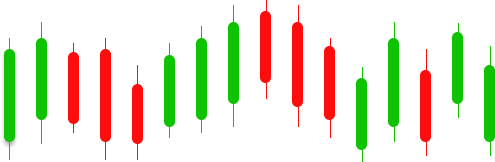
A Mitigation Block is a specific price zone or candle on a chart where smart money or institutional traders previously influenced the market but left some orders unfilled. Later, the price returns to this zone to “mitigate” or fill these leftover orders, allowing institutions to adjust their positions or manage risk.
It often appears as the last up candle before a strong downward move (bearish mitigation block) or the last down candle before a strong upward move (bullish mitigation block).
This zone acts as a magnet for price and provides high-probability trade setups.
2. Why Do Mitigation Blocks Matter?
Institutional Footprints: They reveal where large players placed orders and later returned to complete or adjust their trades.
Supply and Demand Refinement: Mitigation blocks are precise zones within broader supply and demand areas where price imbalance occurred.
High-Probability Entries: Price often reacts strongly when revisiting these blocks, offering good risk-reward trade setups.
Risk Management: Stops can be placed just beyond these zones, allowing tighter and more logical stop-loss placement.
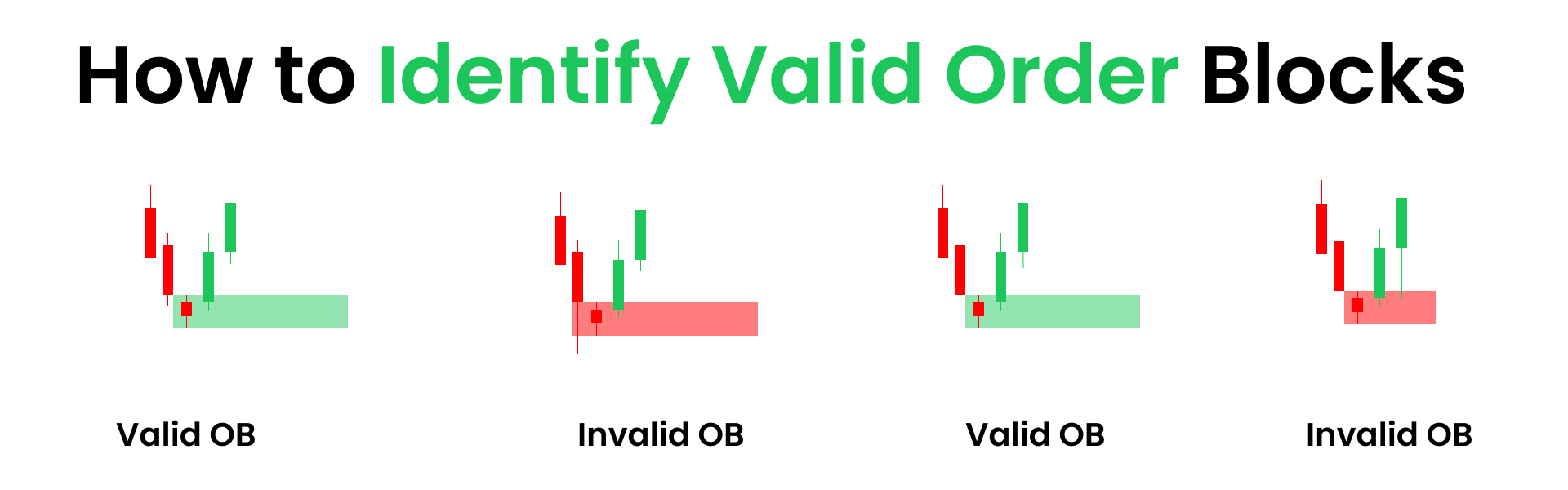
3. How to Identify Mitigation Blocks
Look for a final consolidation candle before a sharp impulsive move.
Identify the last up candle before a strong drop (bearish mitigation block) or the last down candle before a strong rise (bullish mitigation block).
These candles often show increased volume or price rejection.
The zone between the candle’s open, high, low, or close can be marked as the mitigation block.
4. Types of Mitigation Blocks
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Bullish Mitigation Block | Last down candle before a strong upward move; acts as support when price revisits. |
| Bearish Mitigation Block | Last up candle before a strong downward move; acts as resistance when price revisits. |
5. How to Trade Mitigation Blocks
Step 1: Mark the Mitigation Block Zone
Identify the candle or small consolidation zone before the impulsive move.
Step 2: Wait for Price to Return
Price often retraces to this zone to fill unfilled institutional orders.
Step 3: Look for Confirmation
Watch for reversal candlestick patterns (pin bars, engulfing candles) or structural shifts on lower timeframes.
Step 4: Enter the Trade
Trade in the direction of the original impulsive move after confirmation.
Step 5: Place Stop Loss
Set stop loss just beyond the mitigation block’s high (for bearish) or low (for bullish) to protect against false breaks.
Step 6: Set Take Profit
Target the next logical support/resistance or liquidity zone.
6. Practical Examples
Bullish Mitigation Block Example: EUR/USD forms a final down candle before a 50-pip rally. When price returns to this candle’s zone, it reacts bullishly, offering a low-risk long entry.
Bearish Mitigation Block Example: Gold prints a final up candle before a $30 drop. Price retraces to this candle’s zone, then reverses downward, signaling a short entry opportunity.
7. Tips for Trading Mitigation Blocks
Combine mitigation blocks with other Smart Money Concepts like order blocks, fair value gaps, and break of structure for higher accuracy.
Use multiple timeframes to confirm the strength of the mitigation block.
Be patient and wait for clear price rejection or confirmation before entering.
Always apply strict risk management and avoid over-leveraging.
8. Summary
Mitigation Blocks are precise institutional order zones where price returns to fill unfilled orders, creating high-probability trade setups. Recognizing these blocks helps traders align with smart money, improve entry timing, and manage risk effectively.
Quick Reference Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Price zone where institutions return to fill unfilled orders |
| Bullish Block | Last down candle before a strong upward move; acts as support |
| Bearish Block | Last up candle before a strong downward move; acts as resistance |
| Trading Signal | Price retracement + reversal confirmation |
| Stop Loss Placement | Just beyond the mitigation block zone |
| Timeframes | All timeframes; higher timeframes preferred |
| Markets | Forex, stocks, crypto, commodities, indices |
| Risk Management | Use stop loss, confirm signals, risk 2% per trade |
Disclaimer
I am not registered with SEBI or any other regulatory authority. The content and strategies shared on UP Forex Academy site are for educational and informational purposes only. Trading involves significant risk, and you should consult with a licensed financial advisor before making any investment decisions.